WHAT’S UP(COMING)! – Observation Calendar Jul-Sep 2025
Source for events and links are In-The-Sky.org, Dominic Ford, Editor. The links provide details for each event including a scale on how difficult they are to observe.
Source for events and links are In-The-Sky.org, Dominic Ford, Editor. The links provide details for each event including a scale on how difficult they are to observe.

The NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory has unveiled its first imagery, showcasing cosmic phenomena captured over just ten hours of test observations. This facility is set to explore significant mysteries of the Universe over a ten-year mission.
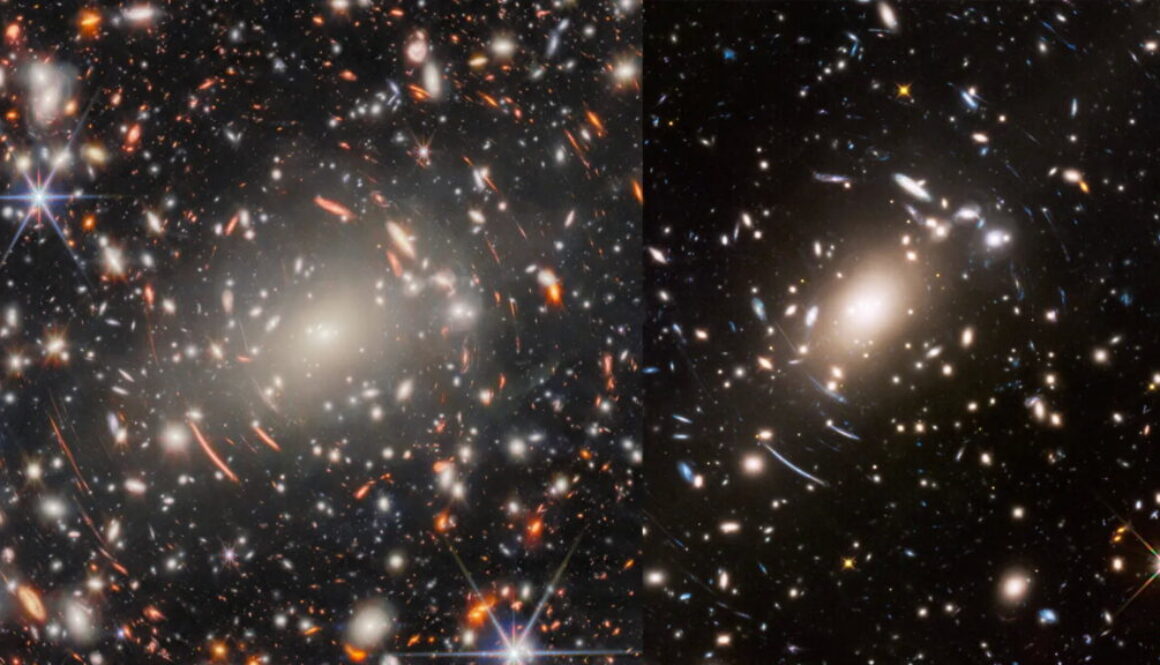

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured its most extreme gravitational lens, revealing the galaxy cluster Abell S1063, located 4.5 billion light-years away, showcasing unprecedented features through deep field observations that highlight the effects of strong and weak gravitational lensing.
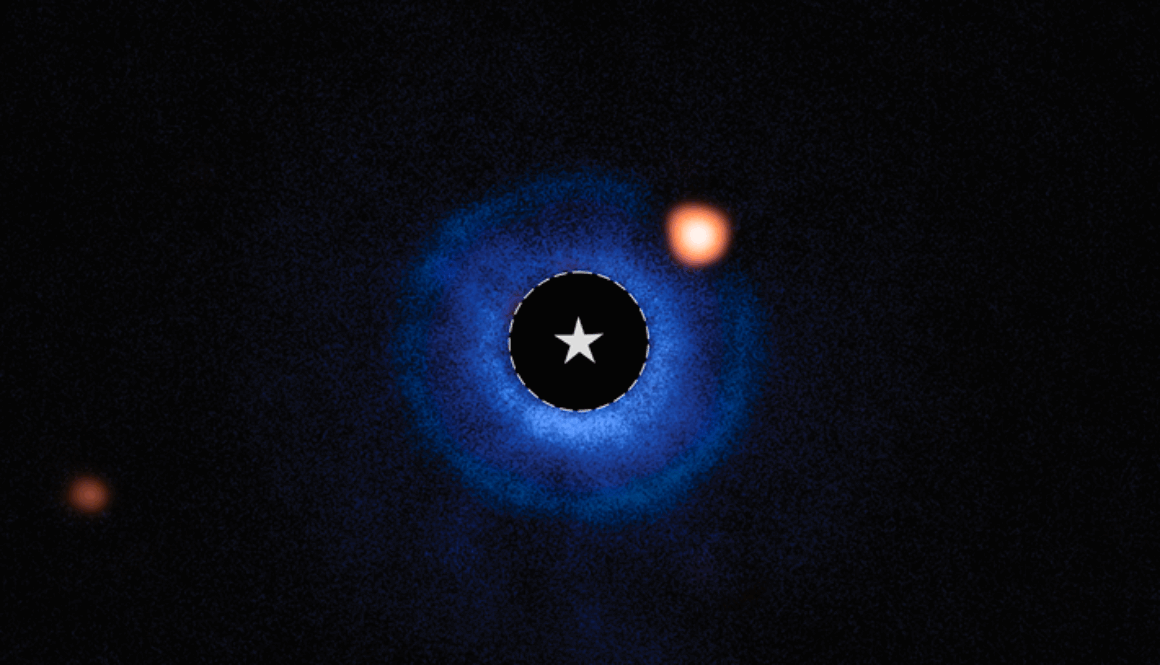
Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have provided strong evidence for a Saturn-mass planet, TWA 7 b, orbiting the young star TWA 7. This discovery, if confirmed, would be the lightest planet ever imaged outside our solar system.
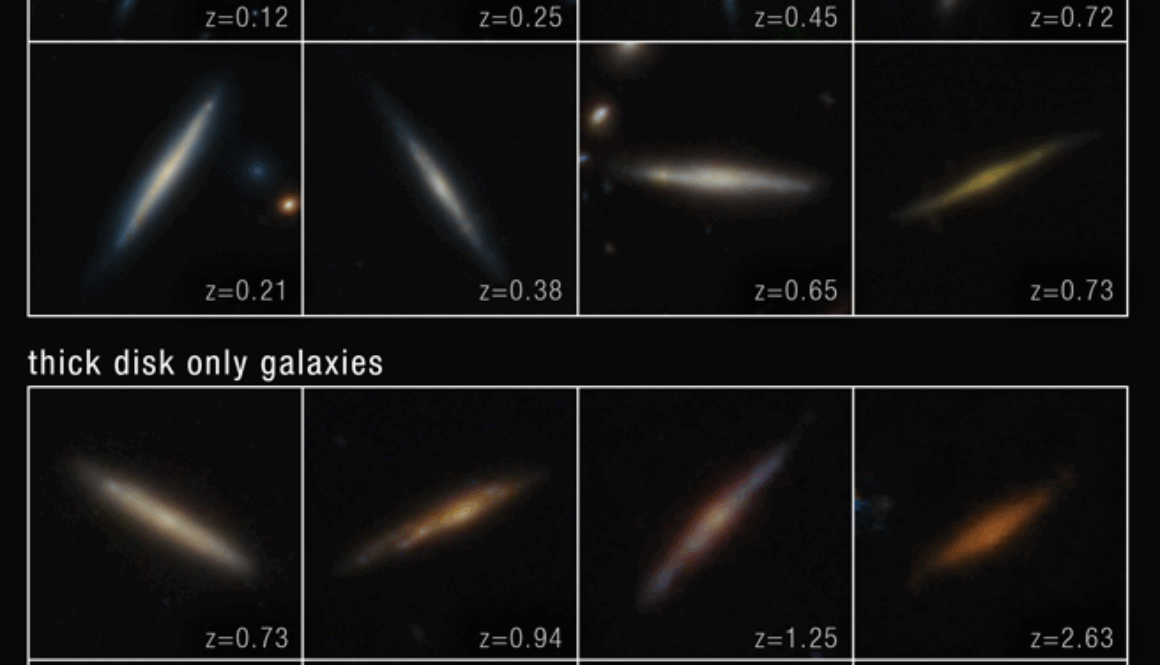

Recent findings have shed light regarding the structural origins of disk galaxies, specifically focusing on the formation of thick and thin disks. Using data from the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers analyzed 111 edge-on disk galaxies, revealing that thick disks form before thin disks, with the timing influenced by the galaxy’s mass.
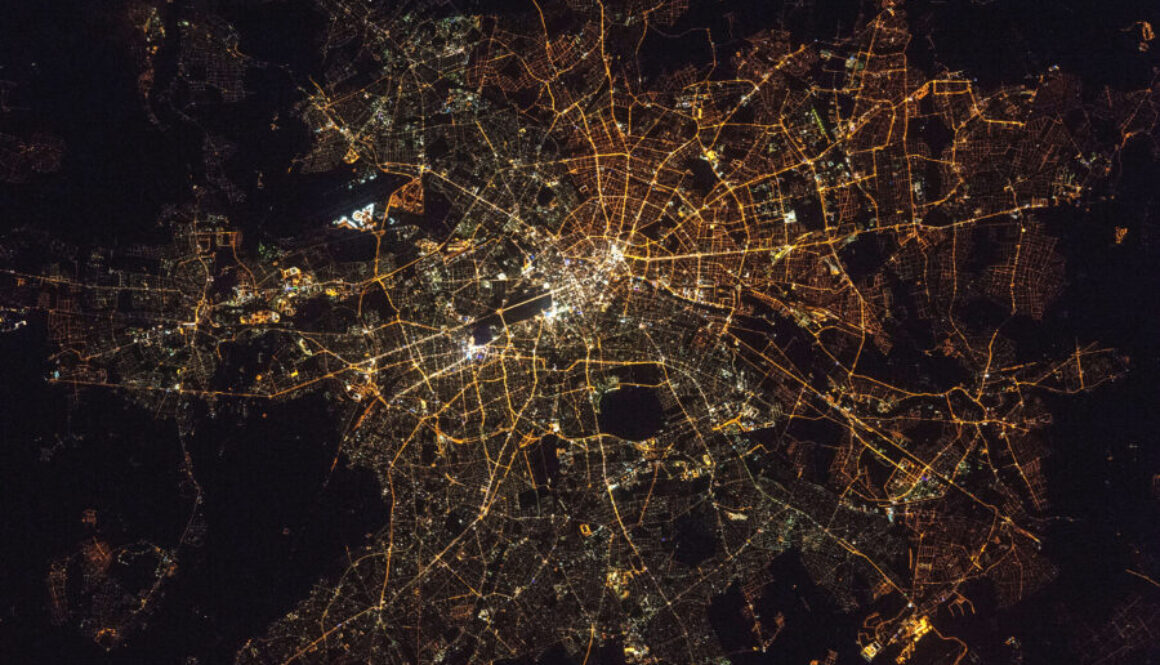

Recent studies indicate that light pollution is increasing by 10% annually, primarily due to private and commercial sources rather than streetlights, which have been converted to energy-efficient LEDs.
This article discusses the search for Population III stars, the first stars formed after the Big Bang, which are difficult to detect due to their lack of heavy elements. New research suggests a shift in focus towards identifying galaxies during their “self-polluted” phase, where heavy elements from supernovae are present, allowing for more detectable signatures while still hosting metal-free stars.